PULMONARY ARTERY CATHETER INSERTION
What is Pulmonary Artery Catheter Insertion?
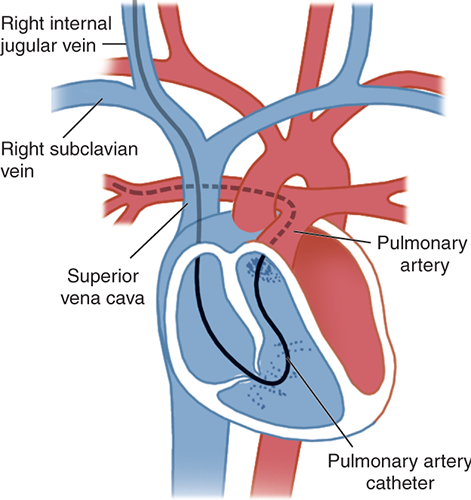
Image Source: https://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=683§ionid=45343692
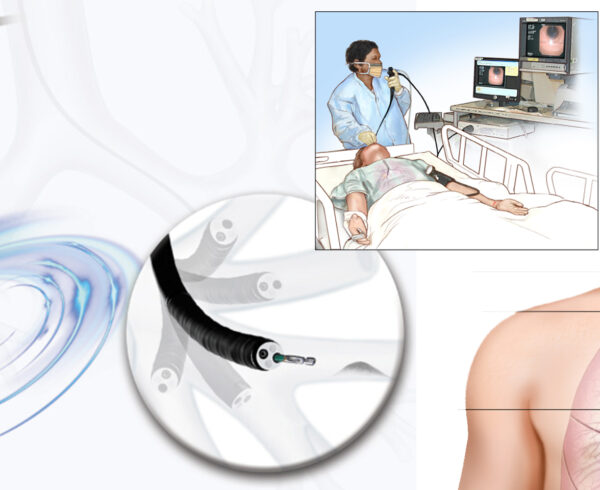
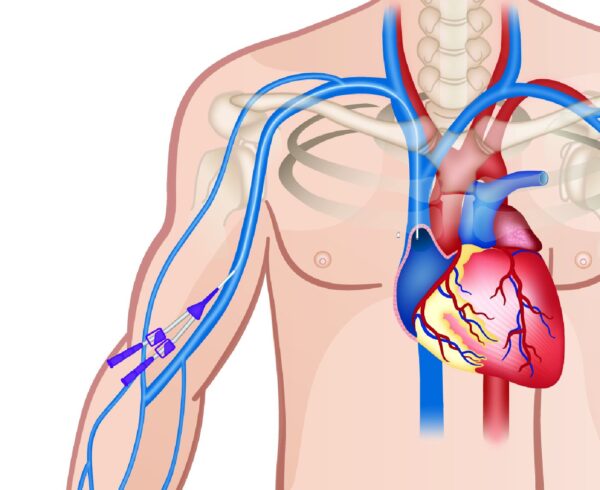
The Pulmonary arterial catheter is a catheter which goes inside the heart into the pulmonary artery to monitor heart and pulmonary arterial pressures.
It can be inserted either via neck veins or via groin veins. It is a complex procedure thus it requires continuous waveform guidance or fluoroscopic guidance to insert it in the exact position.
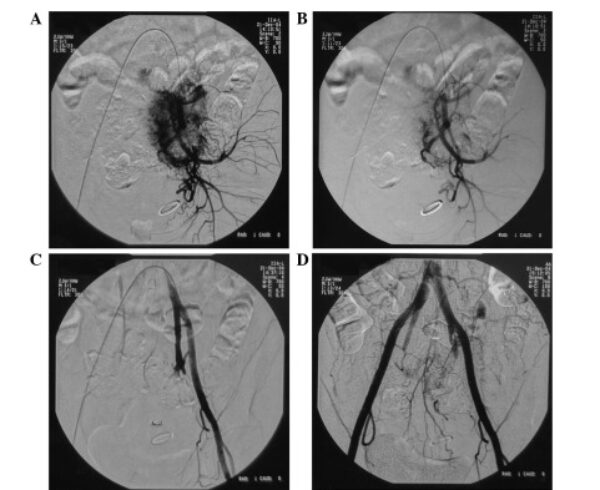
The Pathway for the placement of Pulmonary arterial catheter
For the purpose of introduction of the PA cath, we need a sheath or an introducer which provides access into the large vein. The PA catheter is then guided into the sheath or introducer using waveforms or fluoroscopy. The inflation of the balloon helps to guide the catheter into the Pulmonary artery via floatation. The PA catheter is usually 110cm long. The main purpose is to get the catheter into the first branch of the pulmonary artery and equalize the pressure by inflating the balloon to get the left-sided heart pressures. The principle of thermodilution or the ficks principle is used and cardiac output is obtained either continuous or intermittently which helps us diagnose and prognosticate the patient.
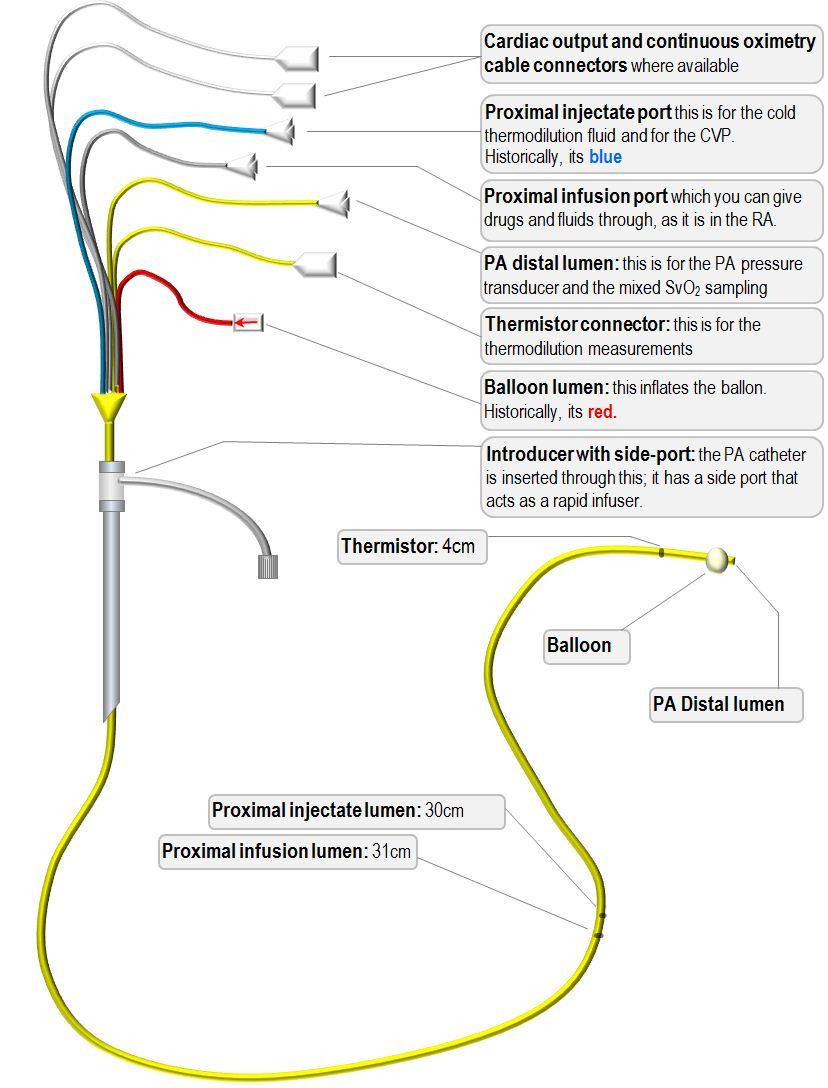
Image Source: https://in.pinterest.com/pin/381117187198177348/
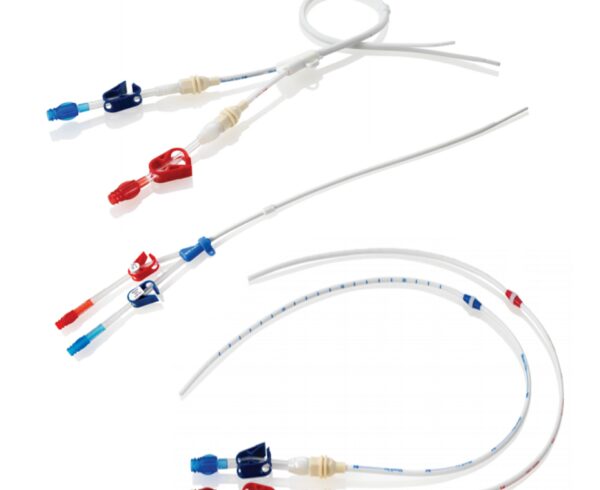
The Pulmonary arterial catheter is either 4 lumen, 5 lumen or 6 lumen. In the 4 lumen catheter
1 lumens is for blood sampling and medications
1 lumen is for PA pressure monitoring
1 lumen is for Balloon inflation
1 lumen is for temperature monitoring
In the 5 Lumen catheter; additional lumen is for Flushing the cold saline to get temperature graph.
In the 6 lumen catheter, an additional lumen is for Thermostat and thermofilament which monitors continuous cardiac output.
Indications:
Because of the expertise required and the complications plus the invasive nature of the PA cath the indications are limited to
Cardio vascular surgeries
Major surgery in the presence of myocardial dysfunction
Combined septic and Cardiogenic shock (As a part of Hemodynamic monitoring)
Procedure
The first step like always will be to obtain informed consent. The patient himself can give the consent but if for some reasons he is unfit to give the consent then the relatives will be asked for the consent.
The next step is to examine the patient and the possible sites which can be used for insertion, the most favored site are the jugular followed by femoral and then subclavian. The sites are examined for ease of access and for the presence of any altered skin or any infection at the site which will negate the insertion at that site. After manual examination, sonographic screening of the vein is done to determine its patency.
The coagulation status of the patient is obtained and if it is deranged then blood products are given to correct it to avoid significant bleeding during the procedure.
The patient is explained about the procedure and then the proceduralist will go for the antiseptic handwash.
After proper handwash and wearing sterile equipment, the patient site is prepared and cleaned with soap and antiseptic like povodine iodine or chlorhexidine in alcohol. Local anesthesia is given in the area of the puncture and then the introducer sheath is inserted via Seldinger technique by threading it over a guidewire.
After the introducer sheath insertion, the PA catheter is threaded over it enclosed inside a sterile sheath. The distal end is connected to a transducer to monitor real-time waveforms for confirming placement. After the optimal position is obtained the sterile sheath is locked over the introducer and sutures are applied to minimize any movements.
Sterile dressing and sutures or StatLock are applied to secure the device and a Chest XRAY is done to confirm the position.
Complications & Problems
Bleeding, arrhythmias as the guidewire enters the heart, Pneumothorax as the lung pleura is in close proximity to the neck, thrombosis, and infections. The most dreaded of complications with the PA cath is the injury to the Pulmonary artery or rupture of the artery which may need intervention from the cardiac surgeon. Also, long term usage and inflation may cause pulmonary infarcts. Thus thorough care is a must and daily screening should be done to evaluate the need to remove the PA cath.


Ask a Question?