DIALYSIS PORT INSERTION
Hemodialysis Catheter Insertion (HD Port)
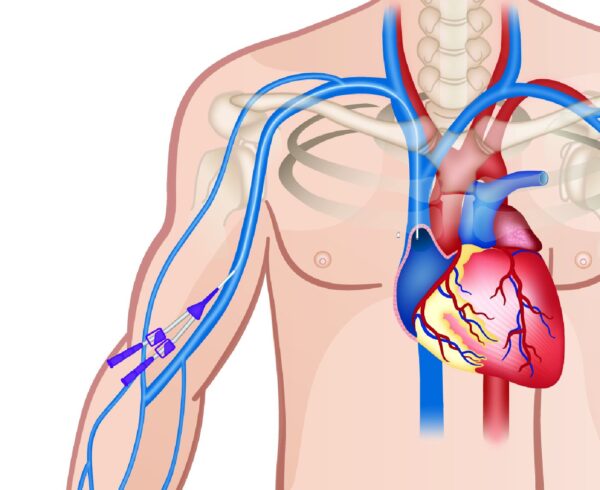
HD port or catheter is a conduit or intravenous access which can be inserted into a large Central vein mainly for the purpose of hemodialysis. The most probable sites are
The Jugular – In the neck; The Subclavian- below the collar bone; The femorals – in the groin.
The best possible access for hemodialysis is either an AV fistula which is artificially created in the arm/ forearm vessels by a surgeon or a permcath which is surgically tunneled into a great vein either of neck or groin. But these procedures require surgical expertise and need to be done in an operative setup. So the HD port is inserted to buy time and get dialysis sessions in the ICU or AKD without any surgical help.
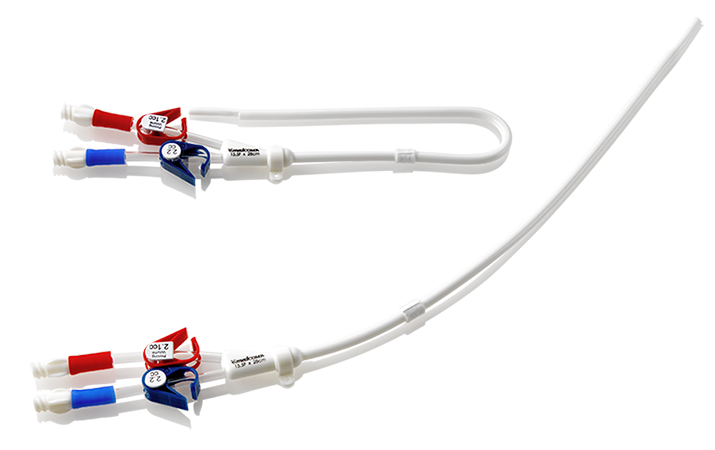

Image Source: http://www.medcompnet.com/products/long_term/titan_hd.html#ordering
The HD port (as shown above)is either Double lumen or triple lumen. The bigger lumens (blue and red)are for the purpose of hemodialysis, one lumen to carry blood towards the dialysis machine and the other to return blood to the patient’s body. The smaller lumen is either for blood sampling via a large vein or administration of irritant and vasoactive medications. It can also be used to measure central pressures if inserted into neck veins.
The HD port is a long catheter with multiple lumens coming out proximally for access. The distal end will be inside the patient. Thus there is a very sterile and systematic procedure for its insertion.
Procedure:
The first step will be to obtain informed consent. The patient himself can give the consent but if for some reasons he is unfit to give the consent then the relatives will be asked for the consent.
The next step is to examine the patient and the possible sites which can be used for insertion, the most favored site are the jugular followed by femoral and then subclavian. The sites are examined for ease of access and for the presence of any altered skin or any infection at the site which will negate the insertion at that site. After manual examination, sonographic screening of the vein is done to determine its patency.
The coagulation status of the patient is obtained and if it is deranged then blood products are given to correct it to avoid significant bleeding during the procedure.
The patient is explained about the procedure and then the proceduralist will go for the antiseptic handwash.
After proper handwash and wearing sterile equipment, the patient site is prepared and cleaned with soap and antiseptic like povodine iodine or chlorhexidine in alcohol. Local anesthesia is given in the area of the puncture and then the central line is inserted via Seldinger technique by threading it over a guidewire.
Sterile dressing and sutures or StatLock are applied to secure the device and a Chest XRAY is done to confirm the position in case of lines in the chest and neck.
Complications and Problems:
Bleeding, arrhythmias as the guidewire enters the heart, Pneumothorax as the lung pleura is in close proximity to the neck, thrombosis, and infections.
Sometimes the HD port does not generate adequate flow which may lead to inadequate dialysis. It usually happens in cases of long term usage or collapsed vein so it might need a readjustment of repositioning.


Ask a Question?