EEG EMG NCS
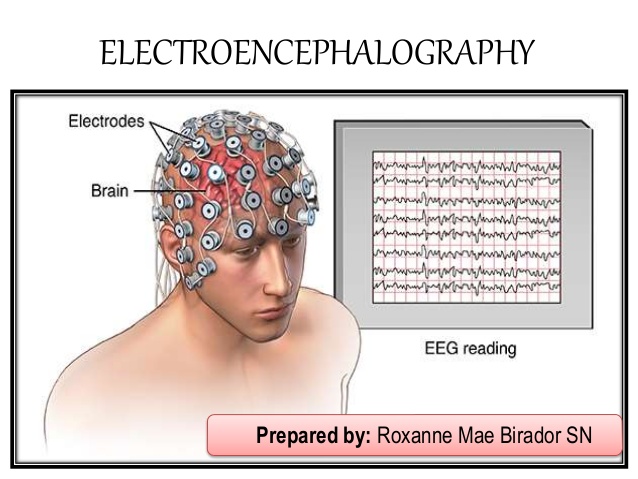
Image Source: https://www.slideshare.net/RoxMae/electroencephalogram-electroencephalography
What is EEG?
EEG (Electroencephalopgram) is a test that detects electrical activity in your brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
Why is it done?
Brain cells are active all the time. These appear as wavy lines in the EEG record just like an ECG (Electrocardiogram) records the activity of the heart.
EEG test may be considered if a patient has fits, unexplained unconsciousness, to assess brain damage, etc
How is it done?
During an EEG, a technician identifies the spots for placement of electrodes and cleans these spots with a cream. Then using a special adhesive paste, the technician attaches the electrode discs on these spots. These discs are connected by wires to the computer equipment which records, amplifies and displays the brain waves.
How does EEG help?
It is useful in a variety of neurological problems ranging from seizures, coma to stroke.
What is EMG and NCS?
Electromyography (EMG) is a test used to study the function of muscles. It is often performed with another test, the NCS (Nerve Conduction Study) which measures how well the signals travel along a nerve.
Why is it done?
EMG and NCS may be considered if a patient has weakness, tingling, numbness, muscle pain, muscle twitching, droopy eyelids, double vision, etc.
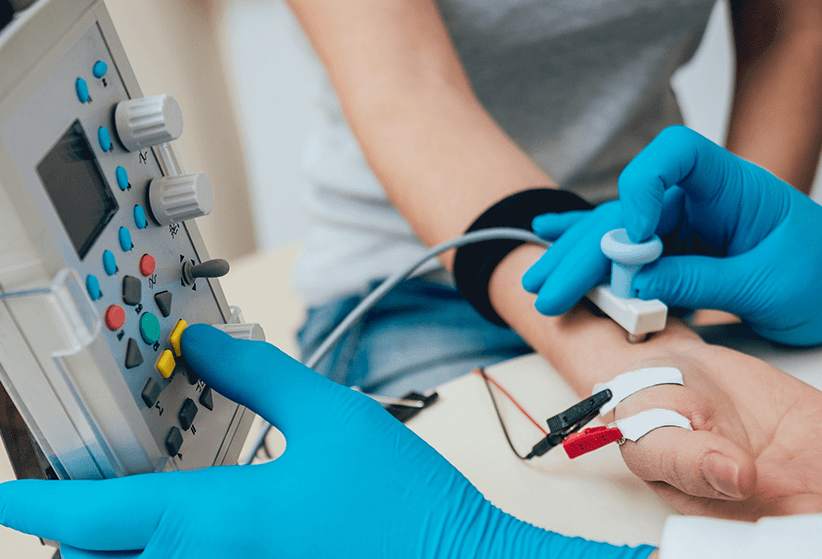
Image Source: https://drjohnshannonalaska.com/emg-nerve-conduction-studies/
How is EMG done?
A needle is inserted in the muscle during a needle EMG. The needle is connected by a wire cable to equipment. The needle contains electrodes which pick up signals from the muscle and these are translated into audio, visual and graphical data on a computer for specialist interpretation. The number of muscles tested depends on the type of problem being evaluated.
How is NCS done?
A hand held device delivers electric pulses to the nerve at different sites along its path. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by surface electrodes (similar to that used for ECG) placed on the surface of the skin at different places along the nerve path. The information is displayed on a computer screen like in EMG for specialist interpretation. The number of nerves tested depends on the type of problem being evaluated.
How does it help?
It is useful to diagnose or rule out conditions such as critical illness neuromyopathy, guillain barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, polymyositis, motor neuron disease.


Ask a Question?