INTUBATION
What is intubation?
Intubation is a process of passing a tube into the breathing pipe [endotracheal tube], to facilitate the breathing process.
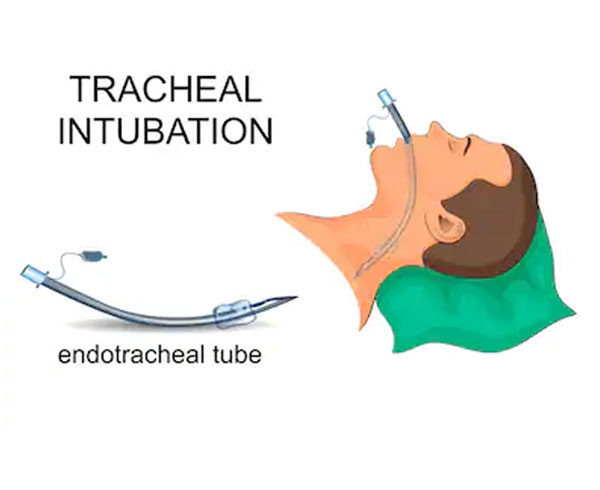
Image Source: https://www.shutterstock.com/search/endotracheal+tube
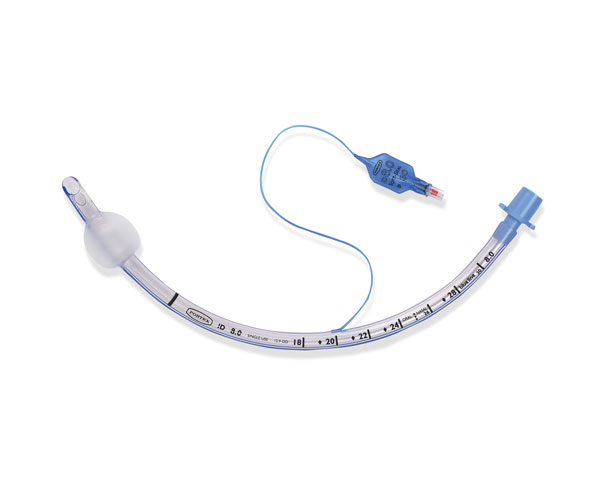
Image Source: https://m.smiths-medical.com/products/airway-management/endotracheal-tubes/cuffed-endotracheal-tubes/endotracheal-tube
How it is done?
It is mostly done electively and many a times its done in an emergency.
When it’s done electively, the patient is sedated and relaxed with medication and with the help of laryngoscope, endotracheal tube is passed into the trachea. It is usually done in the Casualty, ICU and Operation theatre.
When it’s done in an emergency condition like a cardiac arrest, patient is intubated without medication since patient is already unconscious. In case of arrest situation, patient is intubated at the site of arrest.
Why it is done?
The goal of intubation is to secure the airway and to control the breathing.
In the Operation Theatre, its done to deliver the anesthesia and to control breathing during the surgery once the patient is unconscious.
In the ICU, it’s done to secure the airway in a drowsy patient and to ventilate the patient who has respiratory failure. Whenever patient needs invasive ventilator support, patients is intubated and ventilated.
In a cardiac arrest condition, it done to secure the airway and to deliver the manual breath till the patient is taken to the ICU and put on ventilator.
Many time it done to facilitate patient transport safely from one place to another place via ambulance.
What is the risk of intubation?
- Endotracheal tube insertion may cause injury to lips occasionally.
- Few patients have hoarseness of voice after intubation which recovers over few days.
- It may cause injury to vocal cords in a difficult intubation situation.
- There may be endobronchial intubation.
- The biggest risk is blockage of endotracheal tube with secretions.
- Sometime puncture of the tube if patient bites the tube.
- The balloon may rupture, which requires change of tube.
- Once patient is intubated, the tube can be removed once patient is fit to breath and cough out secretions efficiently. Till this is not achieved tube can’t be removed.
- Prolonged intubation increases the risk of infection.
- It may cause weakening of trachea occasionally if the tube is need for very long time.
What is the benefit of intubation?
- It facilitates ventilation process and gives rest to diseased lungs.
- It gives an access for tracheal toileting.
- It given an access for delivering the anesthesia.
- It gives an access for bronchoscopy.
- It prevents oral secretions to drain into the lungs and prevent infection.
- It prevents aspiration.
What is the alternative of intubation?
- Non-invasive ventilation with BiPAP is an alternative to intubation in case of difficult intubation or advance cancer patient.
- High flow nasal cannula is also an alternative to avoid intubation in selected cases.
- Elective Tracheostomy when prolong ventilation or tracheal toileting is needed.


Ask a Question?