VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM (VTE)
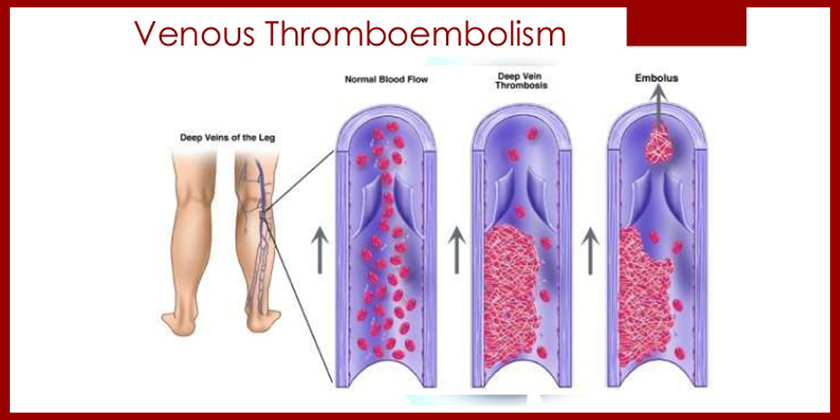
Image Source: https://desdaughter.com/2016/12/01/testosterone-treatment-and-risk-of-venous-thromboembolism/
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
Venous thromboembolism or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms.
These are not infrequent occurrences in the hospital, especially in the intensive care unit.
There are multiple factors that increase the risk of DVT in hospital:
Major general surgery
Major orthopaedic surgery
Lower-extremity paralysis due to spinal cord injury
Fracture of the pelvis, hip or long bones
Multiple trauma
Cancer
Prior VTE— Patients with a previous episode of VTE have a high chance of recurrence.
Age— Patients older than 40 years are at higher risk, and that risk doubles with each subsequent decade.
Obesity— people with obesity have 2 times the risk of VTE as people with normal weight, and the higher the weight, the higher the risk.
Immobility— Prolonged immobility combined with other major risk factors increases the likelihood of VTE.
Oral Contraceptives or oestrogen treatment for menopause symptoms
Family history of VTE— especially if this is in a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, child)
Physical inactivity
Genetic blood conditions that affect clotting
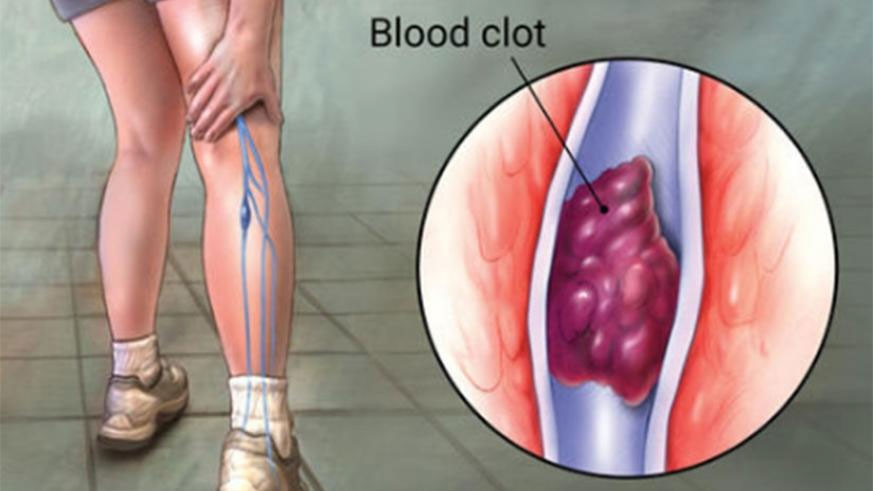
Image Source: https://www.newtimes.co.rw/section/read/220945
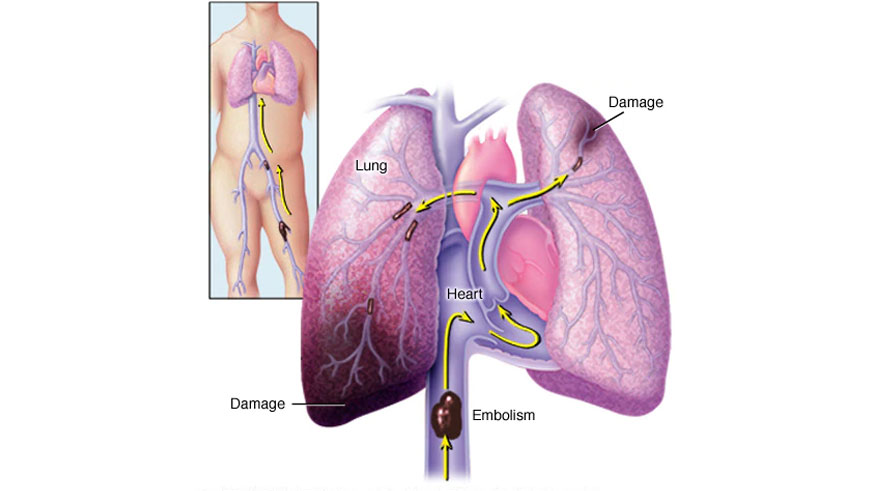
Image Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-embolism/symptoms-causes/syc-20354647
Deep vein thrombosis signs and symptoms can include:
Swelling in the affected leg. Rarely, there’s swelling in both legs.
- Pain in your leg. The pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or soreness.
- Red or discolored skin on the leg.
- A feeling of warmth in the affected leg.
Deep vein thrombosis can occur without noticeable symptoms.
If left untreated, this clot can travel upto the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism (PE) which can be life-threatening.
Hence, in hospital, with any of the above risk factors, patients are risk stratified and given prevention/prophylaxis.
These include:
- Stockings
- Flowtron pumps which are strapped to the calf muscles of the patient
- Heparin injections.
If a DVT +/- PE is confirmed
then the treatment for this if Heparin injections (blood thinners) to begin with and followed by anti-coagulation tablets. The older tablets are Warfarin and Acitrone, which require regular blood tests for monitoring and adjusting dose. The newer medications eliminate the need for dose adjustment and testing.


Ask a Question?