PHYSIOTHERAPY IN ICU
What is the Role of Physiotherapy in ICU?
The ICU is a dynamic interprofessional environment where Physiotherapists assess, treat and manage respiratory conditions, and mobility issues and rehabilitate critically ill patients.
Physiotherapist is involved in specific patient positioning, suctioning, mobilization including ambulation and airway clearance techniques.
The role of Physiotherapy in ICU is split into two broad areas:
Respiratory care
Rehabilitation
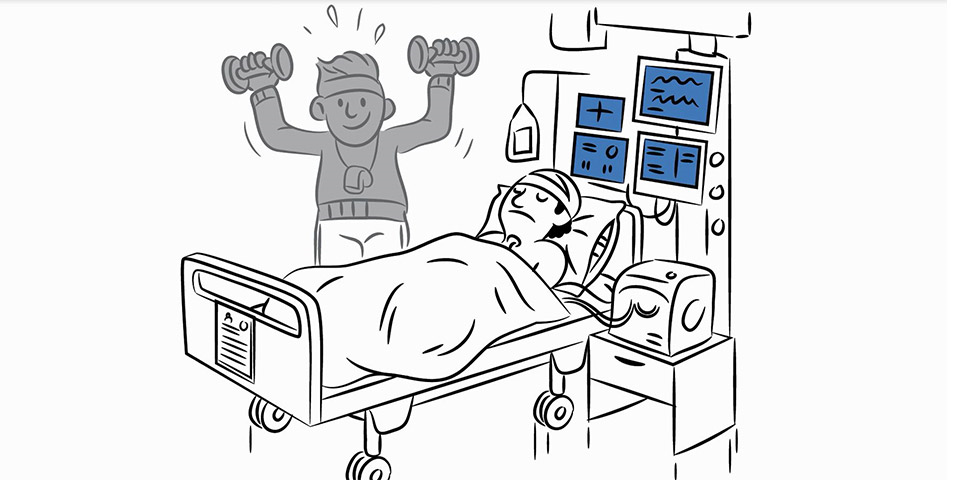
Respiratory Care:
Positioning should be an integral part in ICU respiratory care. Simply turning from supine to side lying can open up collapse lung & improve arterial oxygenation. A 2 hourly position change has been recommended.
Postural drainage is thought to use gravity to assist drainage of secretions. Patients are positioned accordingly the area of lung to be drained.
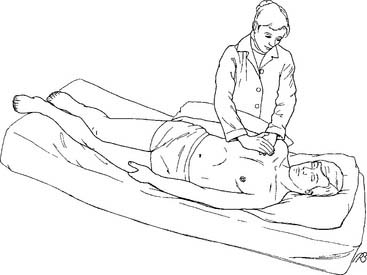
Percussion & vibration are performed by hands in postural drainage position. They aim to loose secretions from the airways wall.
Effective coughing can be assisted by Physiotherapist to remove secretions.
Suctioning may be required to clear secretions for patients who are semiconscious, on ventilator.
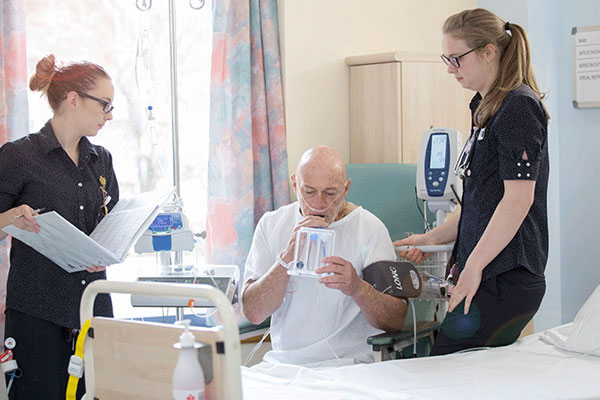
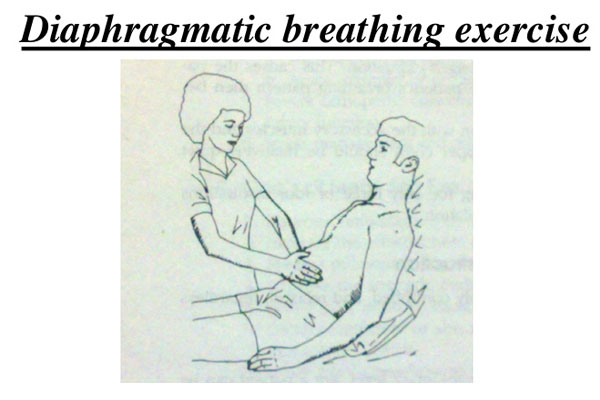
Breathing retraining helps in weaning patients from ventilator. Breathing exercises & Incentive spirometer can help to improve breathing capacity in conscious patients.

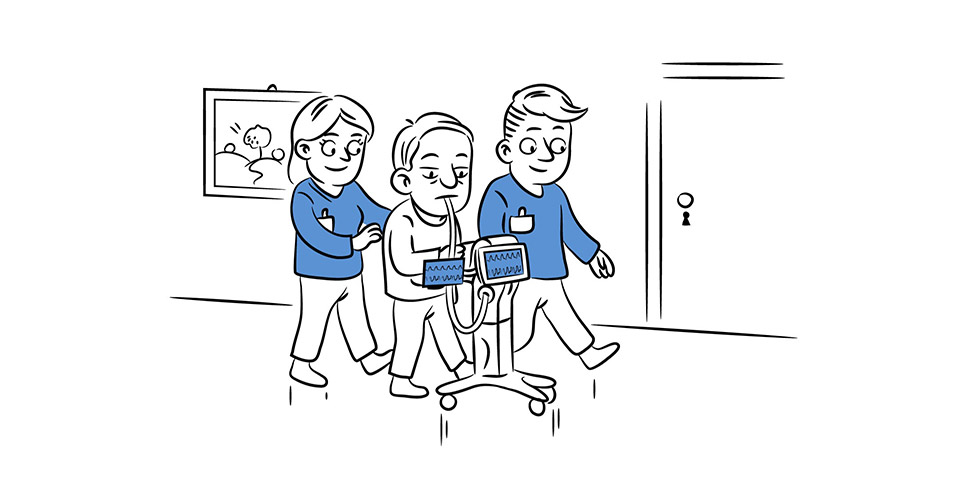
Rehabilitation:
Bed mobility (active or passive) exercises can be started to patients who are confined to bed.
Passive stretching & splinting to hands & feet helps to prevent contractures & joint stiffness.
Resistance training of arm & leg muscles helps to improve muscle strength & function.
Side sitting – Patient needs to spend more time in sitting with their legs dangling over the edge of bed to improve postural control.
Transfer training – Patient needs to mobilize more often from bed to chair. An attempt should be made to stand & walk all patients for whom there is no contraindication such as cardiovascular instability.
Walking should be brief to prevent fatigue with or without walker. Patient who are unable to walk can be mobilized on wheelchair. Early mobilization helps in faster discharge from ICU.
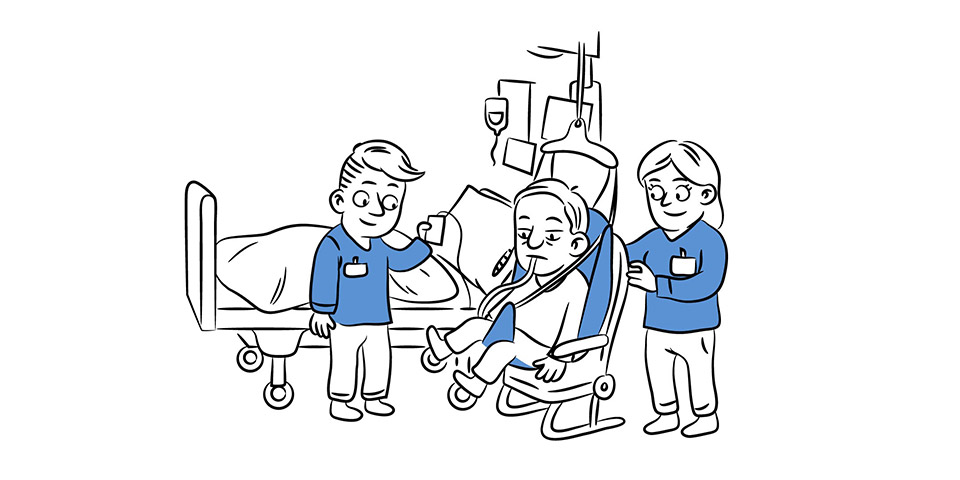
What if Physiotherapy is not Given in ICU?
Physical inactivity leads to deconditioning which causes muscle atrophy & weakness.
Respiratory muscle weakness due to prolonged mechanical ventilation.
Weaning failure.
Pressure sores, bed sores.
Deep vein thrombosis.
Compromised respiratory function like chest infection, pneumonia, lung collapse.
Prolonged length of stay in ICU.
Increased cost of hospitalization.


Ask a Question?